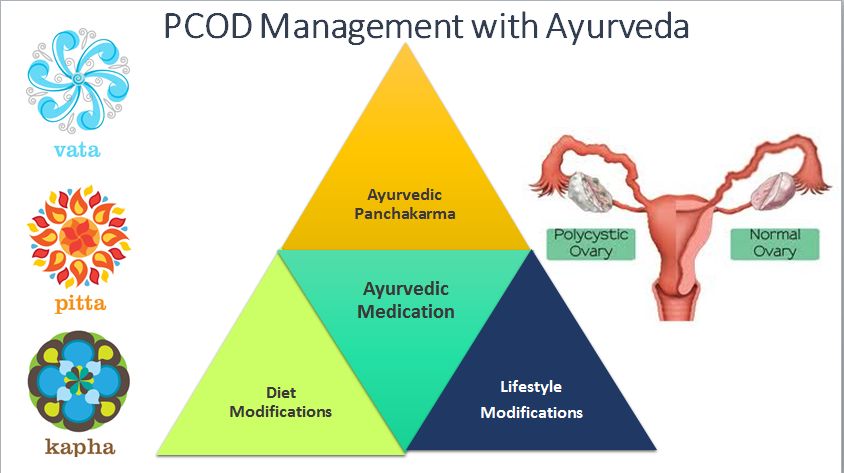
What is PCOS ?
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS, polycystic ovary syndrome) is a relatively common hormonal disorder that causes a number of different symptoms in women of reproductive age. Common to all women with PCOS is an irregularity in the menstrual cycle and the presence of excess male hormones (androgens).The condition was named because of the finding of enlarged ovaries containing multiple small cysts (polycystic ovaries). Although most women with PCOS have polycystic ovaries, some affected women do not. PCOS has also been referred to as Stein-Leventhal syndrome and polycystic ovarian syndrome.