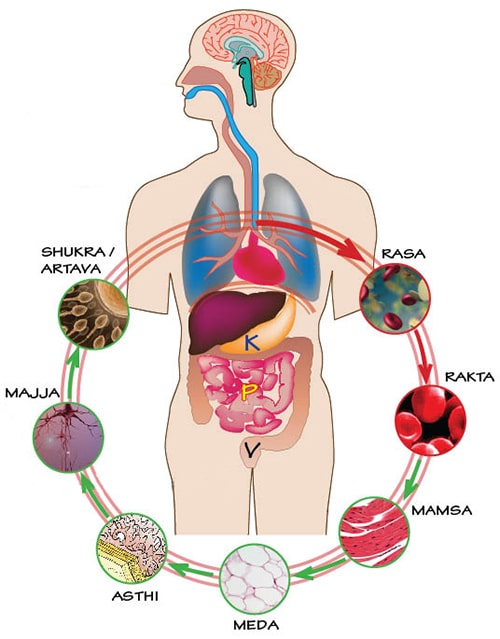
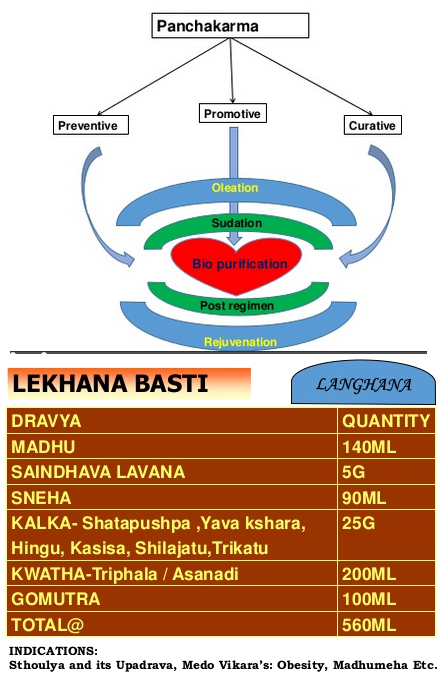
- Ayurveda recommends the use of Guggul as treatment of high levels of lipids in the blood (hyperlipidemia). One tablet, twice a day is recommended for six months for reducing high cholesterol levels in blood.
- In a study the pharmacological effects of Guggul was compared with clofibrate. Ether extract of Guggul (1.5 gms/day) was given to 41 patients. On the other hand, clofibrate (92 gms/day) was prescribed to 10 patients. It was concluded that both the drugs were equally effective in controlling serum cholesterol and triglycerides. Incidence of reported side-effects was less with Guggul
- Fifty patients with a history of coronary artery disease, hyperlipidemia and obesity were treated with daily doses of 10-15 rams of Guggul for three months. After completion of the study, 25 percent reduction in serum cholesterol and 30 percent reduction in serum triglyceride were observed.
- Benefits of guggulu :
- Guggulu supports normal cholesterol levels
- Helps maintain normal weight
- Supports normal lipid levels and metabolism
- Supports normal immune system function
Dosage: 01 capsule twice a day before meals.